Blockchain Technology: Foundations, Trends & Practical Guides
When working with Blockchain Technology, the underlying framework that enables decentralized digital ledgers, smart contracts, and tokenized assets. Also known as distributed ledger technology, it forms the backbone of modern crypto ecosystems. A Decentralized Exchange (DEX), a platform that matches buy and sell orders directly on-chain without a custodian showcases how blockchain removes middlemen, while a Smart Contract Wallet, a programmable wallet built on account abstraction that can handle gasless transactions and social recovery demonstrates the next level of user‑centric security. Blockchain technology encompasses these innovations, requires robust consensus mechanisms, and is influenced by emerging security standards like quantum‑resistant algorithms. Together they shape the future of finance, gaming, and data marketplaces.
Key Topics Covered
Every blockchain transaction starts in the mempool, a waiting area where miners or validators pick which jobs to confirm. Mempool priority depends on fee bids, transaction size, and network congestion, so understanding how miners rank jobs can shave minutes off confirmation times. This dynamic ties directly back to the core protocol’s fee market, a crucial piece of blockchain technology that balances user demand with network security. Mastering mempool mechanics gives you a tactical edge when moving assets on Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Security never stays static. As quantum computers near practical capability, traditional elliptic‑curve cryptography faces a serious threat. Quantum‑Resistant Algorithms, cryptographic schemes designed to survive attacks from quantum processors are being standardized by NIST, with candidates like CRYSTALS‑Kyber and Dilithium already entering testnets. Integrating these algorithms into blockchain protocols influences consensus design, key management, and future‑proofing strategies, ensuring that blockchain technology remains trustworthy even in a post‑quantum world.
Scalability is another hot topic, and state channels provide a practical answer. By opening a private off‑chain ledger between participants, you can settle dozens or hundreds of micro‑transactions instantly, then submit a single settlement proof to the main chain. This approach powers solutions such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and similar scaling layers for Ethereum. Understanding how to open and close state channels equips developers with tools to build high‑throughput applications without sacrificing the security guarantees of the underlying blockchain.
Real‑world projects illustrate how these concepts converge. Take Quadrant Protocol (EQUAD), a data‑marketplace built on a proof‑of‑authority blockchain. It leverages dual‑token economics, smart contract wallets for data buyers, and DEX‑style liquidity pools to trade data assets. Examining such use cases shows how blockchain technology can power niche ecosystems while reusing the same building blocks—consensus, smart contracts, and token standards—that power mainstream DeFi.
Below you’ll find a curated collection of deep‑dive articles that walk through each of these areas step by step. Whether you’re looking to tweak your transaction fees, experiment with quantum‑safe cryptography, or build a state‑channel‑enabled dApp, the guides here will give you actionable insights and clear roadmaps.
Reputation Systems and Sybil Resistance in Blockchain Networks
Sybil resistance is the backbone of trust in blockchain networks. Without it, fake identities can hijack votes, drain funds, and break decentralized systems. Learn how reputation systems, economic incentives, and zero-knowledge proofs keep Web3 secure.
Digital Signatures vs Traditional Signatures in Crypto: How Blockchain Relies on Math, Not Ink
Digital signatures in crypto use math to prove ownership, not ink. Unlike handwritten signatures, they’re tamper-proof, automated, and legally binding - making them essential for blockchain security.
Future of Real World Asset Tokenization: How Blockchain Is Changing Ownership
Real World Asset tokenization turns physical assets like real estate and gold into digital tokens on blockchain, unlocking liquidity, fractional ownership, and global access. Major institutions are already adopting it - and the market could hit $30 trillion by 2034.
zk-STARKs vs zk-SNARKs: Which Zero-Knowledge Proof Is Right for Your Blockchain Project?
zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs are the two leading zero-knowledge proof systems in blockchain. This guide breaks down their differences in security, cost, scalability, and real-world use to help you choose the right one for your project.
Social Token Platforms and Tools: How Creators Are Building Their Own Digital Economies
Social token platforms let creators turn fans into stakeholders using blockchain-based tokens. Learn how Rally, Roll, and others are enabling $450M+ in creator revenue-with real examples, platform comparisons, and what to avoid in 2026.
- 15
- Read More
Future of HSM in Crypto Industry: How Hardware Security Modules Are Shaping Crypto Security in 2026
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are the silent guardians of crypto security. In 2026, they're mandatory for exchanges, evolving with quantum resistance and AI, and shaping how digital assets stay safe.
- 15
- Read More
Diversifying Across Blockchain Sectors: Where to Invest and Why It Matters in 2026
Diversifying across blockchain sectors means spreading your focus beyond crypto into finance, healthcare, energy, real estate, and more. In 2026, this is the smartest way to invest and build with blockchain technology.
- 17
- Read More
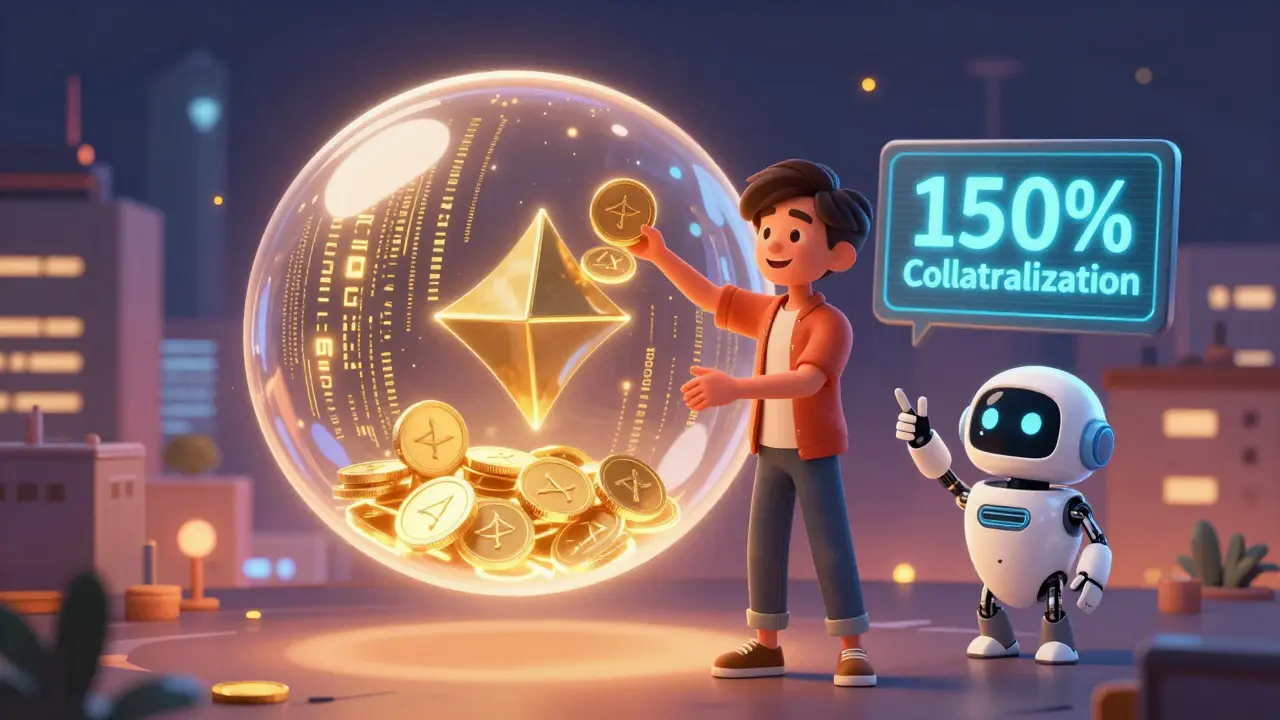
What Is Collateralization in DeFi? A Clear Guide to How It Works and Why It Matters
Collateralization in DeFi lets you borrow crypto by locking up more value as security. It's trustless, global, and fast-but risky during market crashes. Learn how it works, why overcollateralization is needed, and how to avoid liquidation.
- 19
- Read More
Copyright Registration on Blockchain: How It Works and Why It’s Not a Replacement for Official Copyright
Blockchain copyright registration gives creators instant, low-cost proof of ownership, but it doesn't replace official government registration. Learn how it works, its legal limits, and why it's still essential for digital creators.
- 21
- Read More
Future of Blockchain Transaction Fees: What to Expect by 2030
Blockchain transaction fees have dropped from $24 to under a cent since 2021. Learn how Layer-2s, stablecoins, and regulation are making crypto payments faster, cheaper, and ready for global use by 2030.
- 23
- Read More
China's Digital Yuan: The World's Largest CBDC Case Study
China's Digital Yuan, or e-CNY, is the world's largest central bank digital currency pilot, handling nearly $1 trillion in transactions. Unlike Bitcoin, it's fully controlled by the People's Bank of China and offers programmable money, offline payments, and state-level oversight.
- 22
- Read More
How TVL Is Calculated in DeFi: A Clear Breakdown of the Methodology
TVL measures how much crypto is locked in DeFi protocols, but its calculation isn't standardized. Learn how it's done, why numbers often mislead, and how to spot real value from inflated stats.
- 17
- Read More